In this post, I’ll walk through the essentials of configuring an AKS cluster to use Argo CD with an NGINX Ingress Controller.
Pre-Requisites
You’ll need:
- An AKS cluster. Here’s a Gist I use to create a simple cluster.
- Helm 3
- Azure CLI
- A Custom DNS/Access to the provider (I will be using Azure DNS)
NGINX Ingress Controller with Let’s Encrypt
I was inspired by this page on the Microsoft docs. We’re going to install the NGINX ingress controller with Let’s Encrypt.
Note: To simplify things, I will use the NGINX image from Docker Hub. The Microsoft Docs walk you through importing the NGINX image into your own container registry, and… for good reason.
Install NGINX Ingress Controller
First, add the NGINX Helm Repository.
helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
helm repo update
Then install the Helm chart,
helm install nginx-ingress ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx \
--namespace ingress --create-namespace\
--set controller.replicaCount=2 \
--set controller.nodeSelector."kubernetes\.io/os"=linux \
--set controller.admissionWebhooks.patch.nodeSelector."kubernetes\.io/os"=linux \
--set defaultBackend.nodeSelector."kubernetes\.io/os"=linux
Install Cert Manager
Now, install the cert-manager Helm chart. Notice: you will have to add the Jetstack helm repository first.
CERT_MANAGER_TAG=v1.3.1
# Label the ingress-basic namespace to disable resource validation
kubectl label namespace ingress cert-manager.io/disable-validation=true
# Add the Jetstack Helm repository
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
# Update your local Helm chart repository cache
helm repo update
# Install the cert-manager Helm chart
helm install cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager \
--namespace ingress \
--version $CERT_MANAGER_TAG \
--set installCRDs=true \
--set nodeSelector."kubernetes\.io/os"=linux
And lastly, create a CA cluster issuer. This will tell cert-manager to issue certificates for certificate requests across the cluster.
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: letsencrypt
spec:
acme:
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
email: [email protected]
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt
solvers:
- http01:
ingress:
class: nginx
podTemplate:
spec:
nodeSelector:
"kubernetes.io/os": linux
EOF
Install Argo CD
Now, for the good part, let’s install Argo CD with a TLS ingress.
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
For example: argocd.yourdomain.com You can get the Public IP of the NGINX Ingress controller by:
$ kubectl get svc -n ingress
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL
nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller LoadBalancer 10.1.0.88 20.120.123.218 80:30101/TCP,443:31968/TCP 5m13s 443/TCP 5m13s
Next, you’re going to deploy the Ingress rules to be able to reach ArgoCD’s UI using HTTPS. Make sure you add an A record on your DNS to the ingress controller.
Note: Change the code snippet below to include your custom domain.
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: argocd-server-ingress
namespace: argocd
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-passthrough: "true"
# If you encounter a redirect loop or are getting a 307 response code
# then you need to force the nginx ingress to connect to the backend using HTTPS.
#
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTPS"
spec:
rules:
- host: argocd.mydomain.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: argocd-server
port:
name: https
tls:
- hosts:
- argocd.mydomain.com
secretName: argocd-secret # do not change, this is provided by Argo CD
EOF
Open your browser with your custom address for Argo. For example: https://argocd.mydomain.com. Note: it can take about 5 minutes for the Let’s Encrypt certificate to be assigned.
Congrats 🎉
To login, get the initial password via a Kubernetes secret. The username is admin
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d
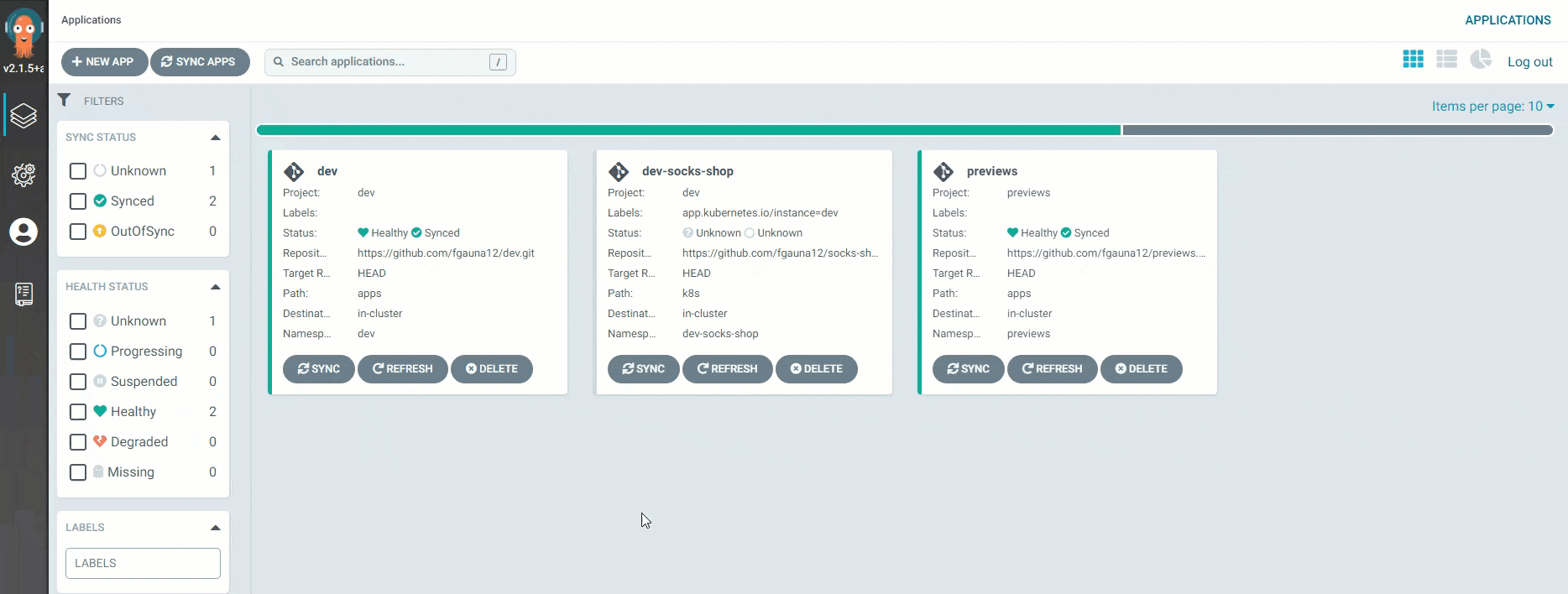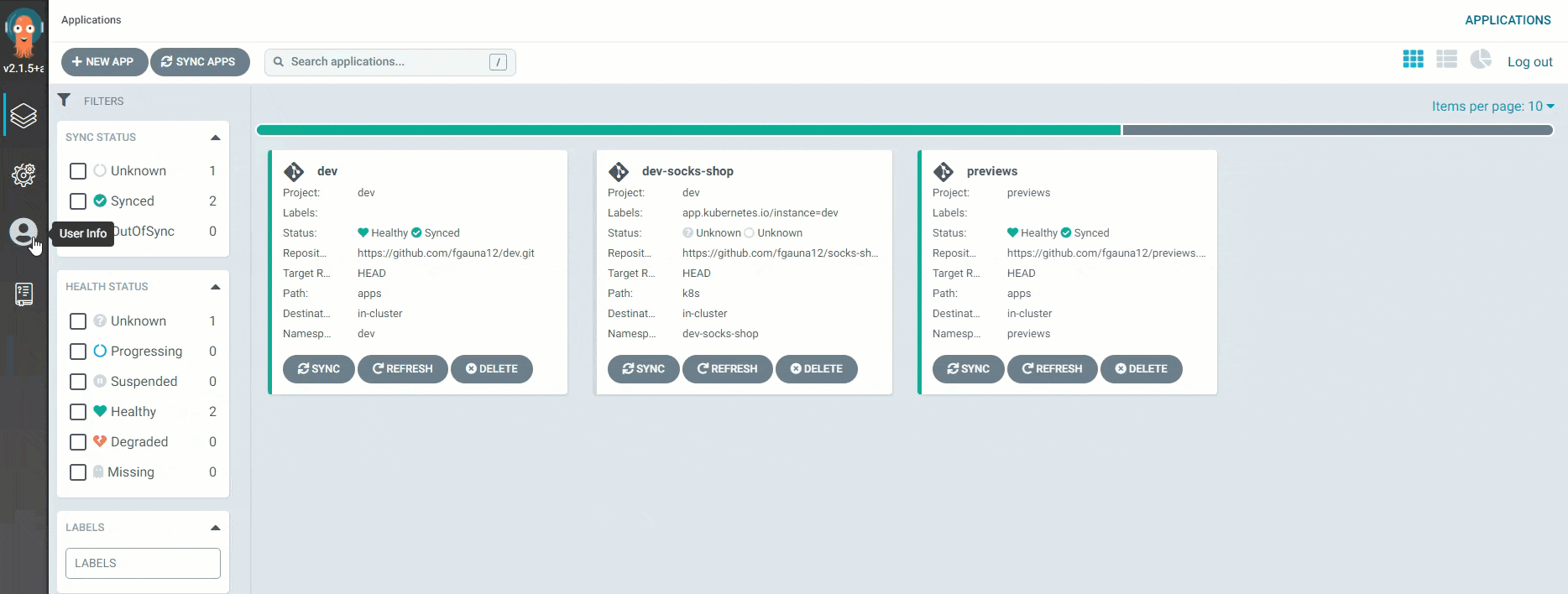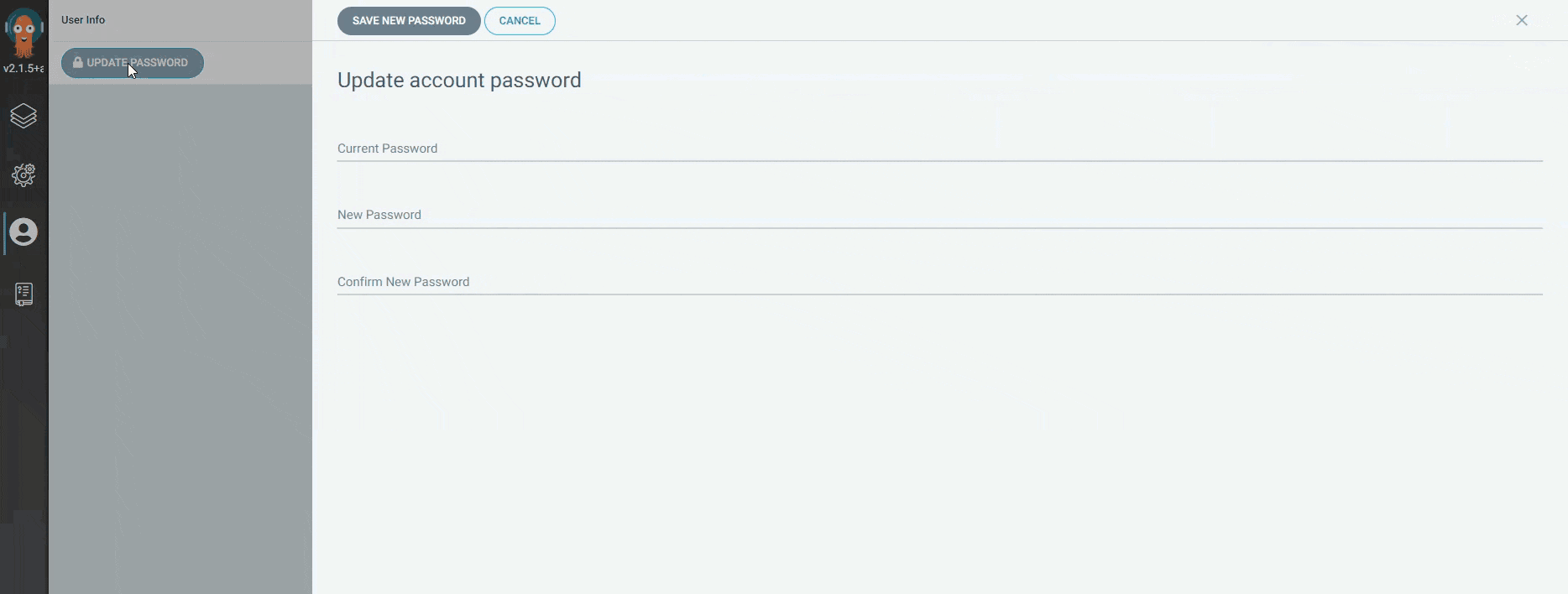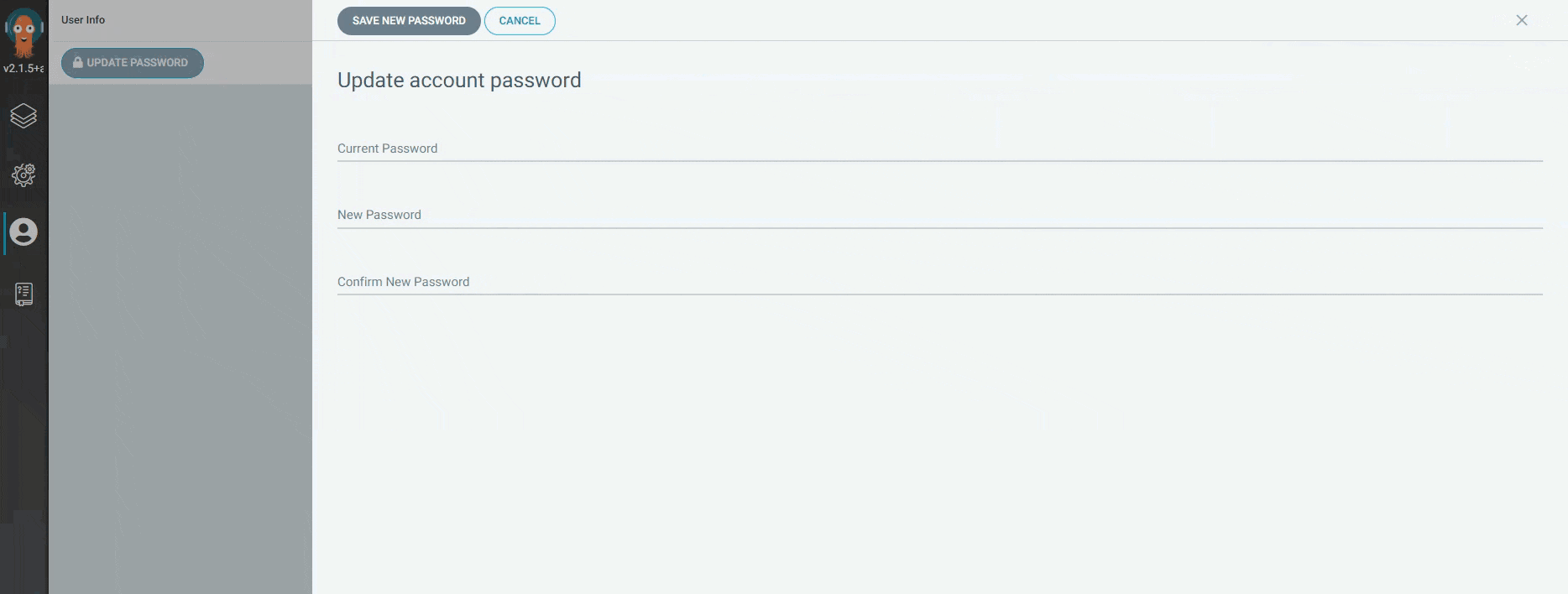
Login to Argo. Then change the default password.
I hope that helped! 🎊