Azure Storage accounts have the capability of hosting static sites. No need for web servers and re-write rules to serve static sites like Single Page Apps. Just drop the static files into Azure Storage and that’s it.
Here’s a quick guide on how to provision an Azure Storage account with static site hosting enabled.
Using Terraform, first declare the provider block. Due to a bug in the provider related to static site hosting, it’s best that you try to use version 2.2.0 or greater.
provider "azurerm" {
version = "~>2.2.0"
features {}
}
Then, I’ll assume you have some variables like this.
variable "app_name" {
type = string
}
variable "location" {
type = string
}
variable "environment" {
type = string
}
locals {
storage_account_name = "st${var.app_name}${var.environment}"
}
Lastly, what’s next is just the Azure Storage resource.
resource "azurerm_storage_account" "storage_account" {
name = local.storage_account_name
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.resource_group.name
location = var.location
account_tier = "Standard"
account_replication_type = "LRS"
account_kind = "StorageV2"
static_website {
index_document = "index.html"
}
}
Notice how we enable static file hosting by declaring the static_website block. In this block, there are some other options like index_document and error_404_document. By setting index_document, Azure Storage will redirect requests to the index page. Otherwise, people would have to hit your URL at /index.html to see the website and would potentially make routes not work.
That’s it!
For those of you new to Azure Storage accounts with static site hosting, it’s essentially a storage account with a container named $web. This $web container will be where the static site is hosted from. Simply, upload your site to this location and you’re done.
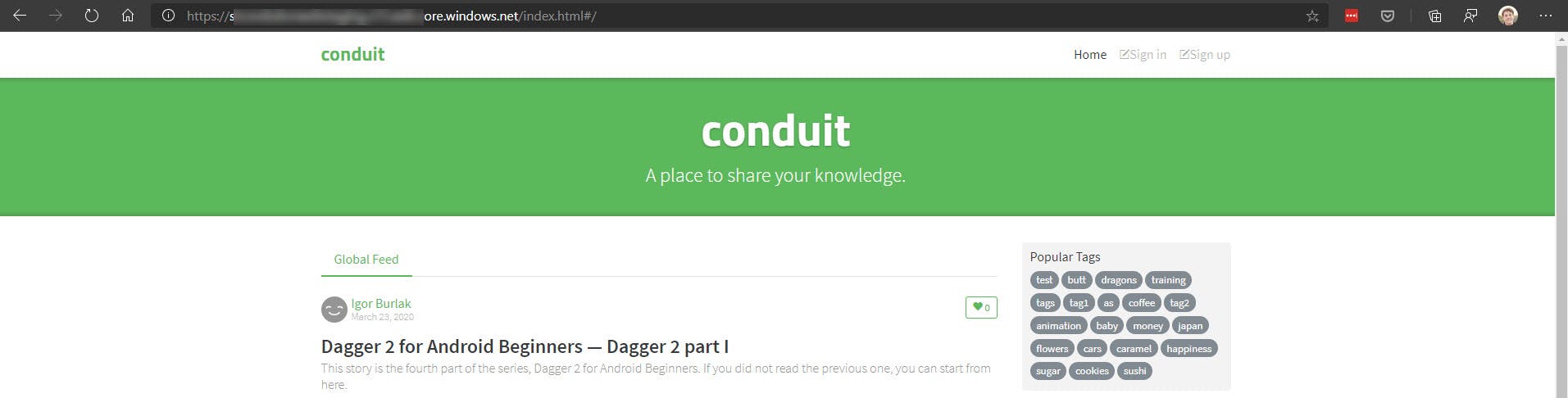
The URL of your website will be under the Static website blade in Azure.